 |
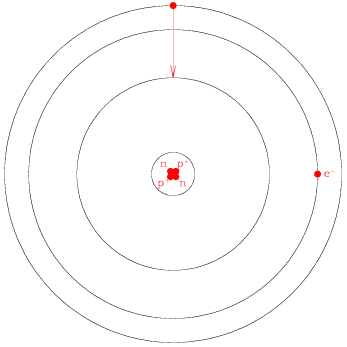
Draw an atom of neutral helium in an excited state below (we have started the sketch for you). Add an arrow showing what happens when the atom emits a photon.
 |
Sort the following in order of increasing energy: infrared, optical, radio,
ultraviolet and x-ray radiation.
[a] ultraviolet, x-ray, radio, infrared, optical
[b] radio, optical, ultraviolet, infrared, x-ray
[c]
radio, infrared, optical, ultraviolet, x-ray
[d] infrared, ultraviolet, x-ray, radio, optical
Which is faster, the speed of light or the speed of sound?
Which is heavier, the nucleus of a hydrogen atom or the nucleus of a helium atom?
Is thermonuclear fission the primary source of the Sun's energy? Why, or why not?
Thermonuclear fission is not the primary source of the
Sun's energy, because there is not sufficient radioactive material
in the Sun to generate the observed amount of energy.
How is helium created in stellar cores (what is the name of the process)?
Helium created in stellar cores through
thermonuclear fusion.
Sketch a continuum spectrum, an absorption spectrum, and an emission spectrum.
The three types of spectra are all
defined by the amount of light emitted as a function of wavelength.
Continuum spectra show emission at all wavelengths, with no breaks,
absorption spectra show emission at most wavelengths with a few
discrete dips at particular wavelengths where light has been absorbed,
and emission spectra show discrete peaks at particular wavelengths
where light has been emitted.
For each of the three spectrum, name an object that gives off light in this form.
See page 97 of Horizons, and lecture notes linked below.
[continuum]
Stellar core
[absorption]
Stellar atmosphere
[emission]
Hydrogen gas cloud
What is the definition of a visual binary solar system?
A visual binary is
a true binary system, where the spatial separation of the two stars is
large enough that we can separate them and observe them each moving in
their orbits.
What is the difference between the progenitor (the star from which it forms)
of a white dwarf and the progenitor of a neutron star?
The progenitor of a white dwarf is a
low mass (less than 8 solar masses) star, and the progenitor of a neutron star is a
high mass star.
What substance will a white dwarf star be made up of, at the end of its lifetime? Diamonds!
What is the true nature of the spiral nebulae, debated by Shapley
and Curtis in 1920?
The spiral nebulae,
or island universes, are simply other galaxies beyond the Milky Way.
What role did Cepheid variable stars play in their arguments?
They used the known relationship between intrinsic
luminosity and period of variation for Cepheid
variable stars to determine the distance to Cepheids observed in
spiral nebulae, to see whether they were located within the Milky Way
or beyond it.
If we found a nearby black hole and sent a scientific probe into it, could
the probe send back information to us on the contents of the central
singularity? Why, or why not?
The probe would not be able to transmit
information from within the singularity,
because the escape velocity within the singularity is greater than the
speed of light and so nothing (mass or light) is able to escape its
gravitational pull.
What are the three primary components of a spiral galaxy?
The three primary components of a spiral galaxy are
the disk, the central bulge, and the diffuse outer halo.
The surface temperature of Pluto is 50 K. The surface of Pluto is thus
[a]
colder than the surface of Venus.
[b] the same temperature as the surface of Venus.
[c] hotter than the surface of Venus.
What is the primary reason for this?
Pluto is much further away from the Sun than is
Venus, and so the amount of sunlight
per unit area is much lower.
What is the wavelength, l, at which Pluto radiates the most energy?
We begin with the blackbody relation (see page 97
of Horizons), relating the temperature T of a blackbody (a body
in equilibrium) with the peak wavelength l where it will emit
most of its energy.
| l (nanometers) | = | 3 × 106 / T (K) |
| = | 3 × 106 / 50 | |
| = | 6 × 104 nanometers |
We can express the wavelength in nanometers, Angstroms, microns, centimeters, kilometers, or meters, or any other unit of length. For practice in units conversion, let's work through a few of these.
There are 10-9 meters in a nanometer.
| l | = | 6 × 10 4 nanometers | |
| = | 6 × 10 4 nanometers | × 10-9 meters / nanometer | |
| = | 6 × 10-5 meters |
| l | = | 6 × 10-5 meters | |
| = | 6 × 10-5 meters | × 106 microns / meter | |
| = | 60 microns |
| l | = | 6 × 10-5 meters | |
| = | 6 × 10-5 meters | × 10-3 kilometers / meter | |
| = | 6 × 10-8 kilometers |
| l | = | 6 × 10 4 nanometers | |
| = | 6 × 10 4 nanometers | × 10-7 centimeters / nanometer | |
| = | 6 × 10-3 centimeters |
| l | = | 6 × 10-3 centimeters | |
| = | 6 × 10-3 centimeters | × 1010 Angstroms / centimeter | |
| = | 6 × 107 Angstroms |
Recall that we can define the amount of energy in light by either its wavelength, l, or its frequency, v, and that the speed of light is 3 × 105 kilometers per second. What is the frequency at which Pluto radiates the most energy?
We begin with the energy relation, relating the amount of radiated energy E in light to either frequency v or wavelength l.
| E | = | h × v |
| = | h × c / l |
This gives us a relationship between v and l.
| v | = | c / l |
| = | 3 × 105 kilometers per second / 6 × 10-8 kilometers | |
| = | 5 × 1012 cycles per second | |
| = | 5 × 1012 Hertz |
Light of this wavelength and frequency has:
[a] a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than optical light.
[b] a shorter wavelength and lower frequency than optical light.
[c] the same wavelength and frequency as optical light.
[d] a longer wavelength and higher frequency than optical light.
[e] a longer wavelength and lower frequency than optical light,
as visible light has a wavelength of 5,000 Angstroms and a frequency of 6 × 1014 Hz.
Extra credit: What is the name for this portion of the electromagnetic spectrum?
A frequency of 5 × 1012 Hertz corresponds
to the infrared (IR) portion of the spectrum.