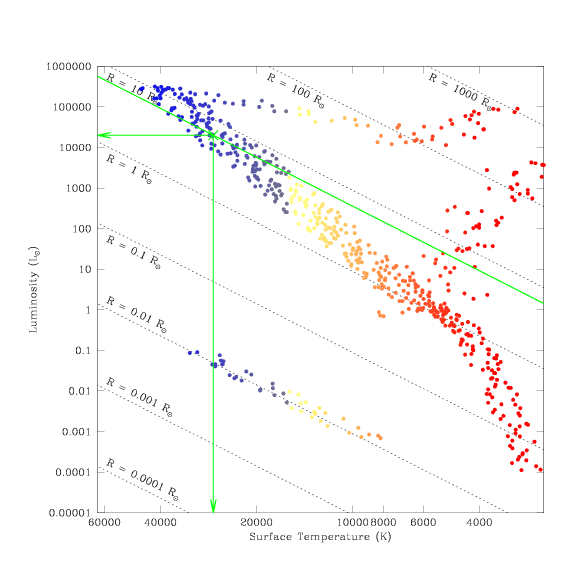
What kind of stars are found here?
A star in this region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram has a temperature of roughly 27,000 Kelvin (27,000 K), a luminosity 20,000 times greater than that of the Sun (20,000 × L_Sun), and a radius six times larger than the Sun (R = 6 × R_Sun). This star lies along the Main Sequence, where most stars (including the Sun) are found. The fairly high temperature indicates quite blue (hot) colours.
Try to read the values of L, T, and R for yourself from the diagram. Do you estimate values for the luminosity, temperature, and size of the star similar to those listed above?

We can use the Stephan-Boltzmann Law to relate the temperature (T), size (R), and luminosity (L) of a star to each other. Measuring L, R, and T in solar units, we say that:
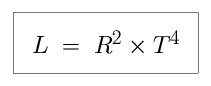
Let us say that the temperature of the star is exactly 27,300 K. We know that the temperature of the Sun is 5,800 K, so we can convert the temperature of the star into solar units. This is just a way of asking How hot is the star relative to the Sun? (If the star is three times as hot as the Sun, for example, T = 3 × T_Sun. If the star is one-third as hot as the Sun, T = 0.33 × T_Sun.)
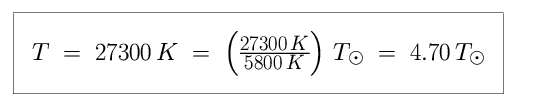
This star is roughly five times hotter than the Sun. The luminosity of the star is 20,000 × L_Sun. (We don't need to convert this luminosity to solar units, as we are already using them.) The final step is to calculate the radius R, from T and L.
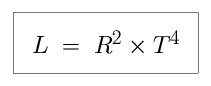
We begin by solving our equation for R. (We need to have R alone, on the left hand side of the equation.) Dividing both sides of the equation by T4,
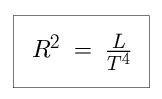
The next step is to take the square-root of each side of the equation.
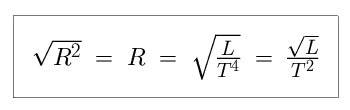
because the square-root of R2 is R, the square-root of L is L0.5, and the square-root of T4 is T4 × 0.5 = T2. We now plug in the values for L and T into the equation, to determine R.
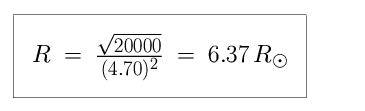
We estimated a value of R = 6 R_Sun from the diagram - an excellent match.