 |
| [NMSU, N. Vogt] |
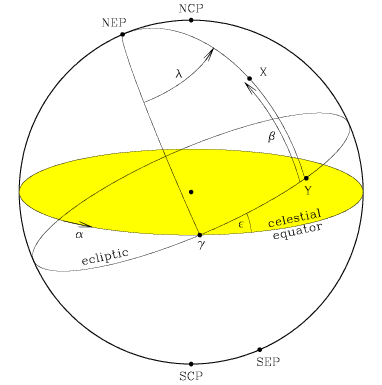
Right ascension and declination are the most commonly used coordinates for objects outside our solar system. In problems dealing with the positions and motions of solar system objects, however, it is often more convenient to refer positions to the mean orbital plane of the solar system using ecliptic coordinates.
Ecliptic latitude,  , is
analogous to declination, but measures the angular distance north or south of
the ecliptic, attaining +90° at the north ecliptic pole (NEP) and
-90° at the south ecliptic pole (SEP). The ecliptic latitude of the star
X is given by the arc YX.
, is
analogous to declination, but measures the angular distance north or south of
the ecliptic, attaining +90° at the north ecliptic pole (NEP) and
-90° at the south ecliptic pole (SEP). The ecliptic latitude of the star
X is given by the arc YX.
Ecliptic longitude, 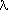 , is
analogous to right ascension (
, is
analogous to right ascension ( )
and is measured from the first point of Aries,
)
and is measured from the first point of Aries, 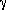 , in the same direction as right
ascension but along the ecliptic rather than the celestial equator. The
ecliptic longitude of the star X is given by the angle between
, in the same direction as right
ascension but along the ecliptic rather than the celestial equator. The
ecliptic longitude of the star X is given by the angle between 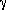 and Y.
and Y.