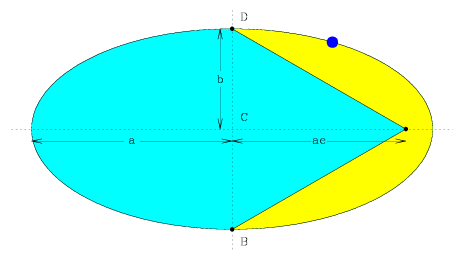
Example: For what fraction of an orbit does a planet lie on the sunside of the minor axis?
 |
| [NMSU, N. Vogt] |
We define e as the eccentricity, and a and b as the semi-major and semi-minor axes. Using conservation of angular momentum, or Kepler's second law, we can equate the areas swept out by a vector between the Sun and the planet per unit time for the yellow shaded region and for the total ellipse.
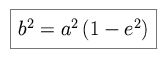 |
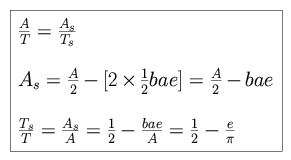 |
 |
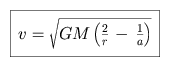 |