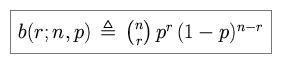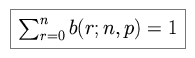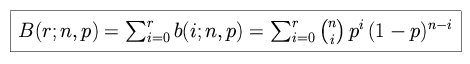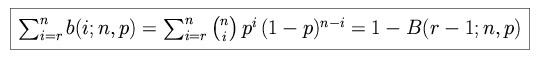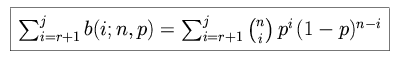The Binomial Probability Law
Consider the case of Bernoulli trials where each individual event
has a binary outcome ( = {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that
= {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that
where
Note the following, achieved by summing over all possibilities.
The probability of r or fewer successes (the binomial distribution function) is
The probability of r or more successes is
The probability of more than r, but less than j, successes is
 = {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that
= {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that
 = {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that
= {0,1}).
We define b(r; n, p) as the probability of getting r successes in
n independent trials, each with independent trial success probability
p. The binomial probability law tells us that