- Easily biased by non-rational use of data.
- All outcomes must be equally likely.
- Cannot handle an infinite number of possible outcomes.
 |
- We must estimate from a finite number of trials.
- We postulate that nE/n approaches a limit as n goes to infinity.
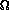 (the set of all outcomes), and an
event
(the set of all outcomes), and an
event 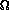 (a subset of the sample
description space which satisfies certain constraints).
(a subset of the sample
description space which satisfies certain constraints).
Consider the following definitions of axiomatic theory:
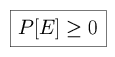 |
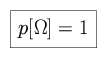 |
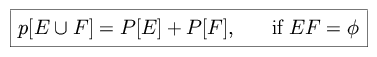 |
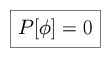 |
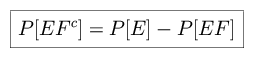 |
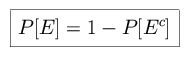 |
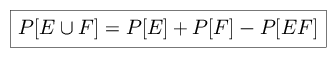 |