- Similar to L dwarf in optical, though somewhat more faint
- Decreasing temperature means carbon more likely to appear as CH4 instead of CO.
- Although L dwarfs do show presence of some CH4 absorption, T dwarfs defined by Kirkpatrick as showing CH4 absorption overtones in H and K band (1.6 and 2.1 µm)
- Cloud structure become very important from L-to-T transition - iron & silicates precipitate out as temperature drops
|
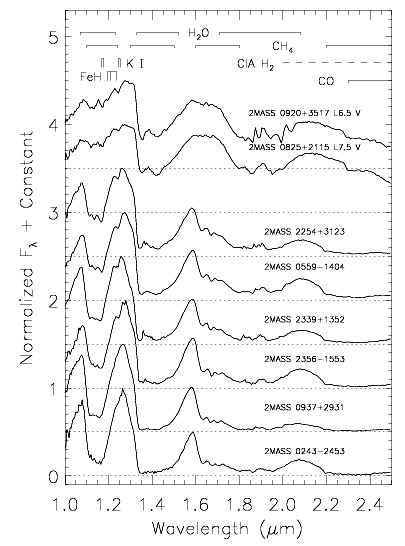
Figure taken from Burgasser (2002).
|

