


Next: About this document ...
PART I - SOLAR SYSTEM
Introduction to Astronomy 110G
Goals for Astr 110G
- Learn Astronomy
- Learn basics of the scientific method: how to study the unknown
- Help you to develop logical thinking skills.
- Develop a broad appreciation for science & its impact on
society.
- Better comprehension & enjoyment of science articles in
the newspaper.
- Improve ability to vote intelligently on science-related
issues.
- Introduce you to a variety of sciences since Astronomy
involves geology, physics, chemistry, & mathematics.
- Have fun observing & looking at the sky with a new found
appreciation of the Universe's attributes.
It's a Big Universe!
Scientific Method and Scientific Models
- New observation or discovery is made
- Make a HYPOTHESIS (a conjecture, a guess, an
assumption).
- It does not even pretend to explain everything; just one
feature, one side of what was found.
- Make new observations
- Build a MODEL: (partial) description of the thing
- (e.g., comet, asteroid, galaxy, quasar)
- Model tries to explain many details.
- Make new observations
- Build a THEORY: a system of rules, which explain the
whole phenomenon. It can be applied for all events of the same kind.
- e.g. a theory, which explains motion of a comet, should be
used for ANY comet.
- Science uses models to understand the Universe around us.
It holds the essence of the scientific method.
- A functional model must:
- explain our observations of the real world.
- predict future observations.
- For example, a model of gravity & the solar system must explain
the positions of the planets in the past and predict where they will be
in the future.
The Solar System
The Planets
- The Solar System consists of 2 kinds of planets:
- The Terrestrial planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, &
Mars. These are Earth-like planets that are small, dense, rocky
worlds with less atmosphere than Giant planets.
- The Jovian planets include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, &
Neptune. They do not have a solid surface & consist mainly of hydrogen
and helium gas.
- Pluto does not really fit either category.
- Density is a key measure of the material which comprises a
planet. It is a measure of how much matter is packed into a volume of
space.
Water has a density of 1 gm/cm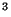 , iron has a density of 7.8
gm/cm
, iron has a density of 7.8
gm/cm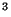 , and rocks have a density of 2-4 gm/cm
, and rocks have a density of 2-4 gm/cm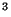 . So, by knowing
the density of a planet, one can roughly determine the internal
composition. The Earth has a density of 5.5 gm/cm
. So, by knowing
the density of a planet, one can roughly determine the internal
composition. The Earth has a density of 5.5 gm/cm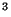 whereas Jupiter
has a density of 1.3 gm/cm
whereas Jupiter
has a density of 1.3 gm/cm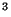 . What does that tell you about the
difference in compositions of these two planets?
. What does that tell you about the
difference in compositions of these two planets?
- Planets also rotate and revolve.
- Planets spin on their axis or rotate. The period of
rotation determines the length of a day. The inclination of a
planet's rotation axis will determine its seasons.
- Planets also revolve about the Sun. The period of
revolution determines the length of a year for that planet. Planets
further from the Sun revolve more slowly than those closest to the
Sun.
Terrestrial Planets:
- Impact craters
- Volcanoes
- Rivers and Canyons
- Plate tectonics
- Moon (not a planet)
- The Moon is 25% of the Earth's diameter.
- Its density is 3.4 gm/cm
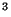 implying a
mostly rocky core (vs. metallic core for the Earth).
implying a
mostly rocky core (vs. metallic core for the Earth).
- It does not have any atmosphere.
- Impact craters: The Moon's surface is heavily cratered.
- Mares
- Mercury
- Mercury is a heavily cratered planet closest to the Sun.
In some ways, it most resembles the Moon.
- The density of Mercury is 5.4 gm/cm
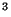 .
.
- Impact craters
- Scarps
- Hot/Cold, no atmosphere
- Venus
- In mass & density, Venus is nearly the Earth's twin.
- Venus' atmosphere is very thick and opaque.
- The atmosphere is about 95% carbon dioxide (CO
 ).
Other components are also present: N, water vapor, sulfuric acid
).
Other components are also present: N, water vapor, sulfuric acid
- Heat is trapped near the planet's
surface by a runaway Greenhouse Effect
that produces a surface temperature of nearly 470
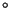 C.
C.
- The planet has been imaged from orbit using the Magellan radar
mapping system. The surface was photographed by the
Russian Venera spacecraft.
- Volcanoes
- Coronae, archnoids, ``pancakes''
- Impact craters: more than on the Earth, but less than on the Moon.
- Earth
- The Atmosphere is 79% nitrogen, 20% oxygen, & 1%
other trace gases.
- The Earth's surface is active, constantly destroyed &
renewed in large sections. This is called plate tectonics.
- Plate tectonics: slow motion of large pieces of crust
- Water and oceans. LIFE !!!
- Mars
- Mars has a mass of about 10% that of Earth.
Its density is 3.9gm/cm
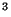 .
.
- The peak surface temperature is nearly
20
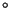 C (but minimum is -140
C (but minimum is -140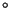 C).
Mars also has polar ice caps (water ice!)
like that of Earth.
C).
Mars also has polar ice caps (water ice!)
like that of Earth.
- The atmosphere is again 95% CO
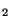 ,
but much thinner than that
for Venus or Earth.
,
but much thinner than that
for Venus or Earth.
- Volcanoes: Olympus Mons
- Canyons: Valles Marineris
- Traces of erosion: dry river beds
- Winds and dust storms
- Polar caps: frozen CO
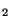
- Underground water ??
Jovian Planets:
- Jupiter
- Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar System.
Its mass is 318 times that of Earth.
Its radius is 11 times that of Earth.
- Jupiter's density is 1.3 gm/cm
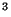 . So, it is composed mainly of
gases with a rocky & (liquid) metallic core.
This core generates a strong
magnetic field (10 times that of Earth).
. So, it is composed mainly of
gases with a rocky & (liquid) metallic core.
This core generates a strong
magnetic field (10 times that of Earth).
- The atmosphere is 79% hydrogen (H), 20% helium (He)
- Alternating zones & belts in atmosphere are produced by
rising & sinking of hot gas (convection).
- Jupiter has many moons (
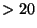 ), including 4 satellites
first discovered by Galileo (Galilean satellites).
), including 4 satellites
first discovered by Galileo (Galilean satellites).
- One moon, Io, has active volcanoes!
- Another moon, Europa, has oceans (icebergs!)
- Saturn
- Saturn is the 2nd largest planet with a mass of 95 times
that of Earth and a radius of 9 times that of Earth.
- Saturn's density is the lowest in the solar system at
0.68 gm/cm
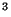 .
.
- The atmosphere is similar to that of Jupiter.
- Saturn is best known for its spectacular ring system
(although all the Jovian planets have rings).
- Saturn also has many moons. Titan is the most
interesting because it has an atmosphere made of 99%
nitrogen that may be similar to that of the primitive Earth.
- Uranus & Neptune
- These Jovian planets are also large and have low
densities of about 1.5 gm/cm
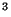 .
.
- The main difference between these planets and
Jupiter is that Uranus & Neptune are composed mainly
of icy materials.
- Composition is 15% H & He, 60% ices,
& 25% Earthy (iron, rocky, etc.).
- Pluto
- Pluto was discovered by NMSU Professor Clyde Tombaugh.
- It is a peculiar tiny planet (18% that of Earth's radius).
Its density is about 2 gm/cm
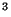 & so is composed mostly
of rocky materials.
& so is composed mostly
of rocky materials.
- A large moon, Charon, was discovered in 1978.
Solar System Debris
- Asteroids are large chunks of rock that lie primarily between
the orbits of Mars & Jupiter. The largest asteroid is named Ceres. Its
diameter is 940 km. Only three asteroids have diameters between greater
than 300km: Ceres, Pallas, and Vesta. About thirty other asteroids have
diameters between 200 and 300 km. Most of asteroids are very small.
- Comets are like dirty icebergs which heat up near the Sun,
partially vaporize, and leave a tail of gas & dust behind them. There
are two reservoirs of comets. Beyond Pluto's orbit extending to 500 AU
there is the Kuper belt, where comet's nuclei move around the Sun close
to the plane of ecliptic. Another place for comets is the Oort cloud,
which extends out at least 50,000 AU, one third the distance to the
nearest star. Most of the comets never (or very rarely) come close to
the Sun.
Structure of a comet:
- Tails form when a comet comes close to the Sun. The
solar wind and sunlight blow comet's gases outward into one or more
tails. Tails can be as long as 100 million kilometers. Tails always
point away from the Sun.
- Coma is a large envelope of gases around the nucleus of
comet. Typical size of coma is 1 million kilometers
- Nucleus is the solid body of a comet. It's typical size is
only few kilometers across.
- Meteors are pieces of rock & ice, coming from asteroids &
comets, which fall into the Earth's atmosphere (so-called ``shooting
stars''). A few large ones strike planetary surfaces & produce impact craters.
The Closest Star: The Sun
- The Sun is the closest example of a star.
- The Sun generates its energy (heat & light) by thermonuclear
reactions at its core.
- Convection: rising bubbles of hot gas
- Convection: granules
- Sunspots and Magnetic fields
- Active Sun: Prominences and Flares
- Every 11 yrs, the Sun undergoes a higher level of activity
including the formation of many sunspots & solar flares.
Measures of Motion
- Gravity causes objects with mass to move. Examples include an
apple falling toward the ground and the Earth going around the Sun. So,
we need to understand a bit about motion.
- Velocity or speed is the rate of change of position
of an object with time. The units of velocity are:
or meters per second (m/sec). When you are cruising down I-25 at
the speed limit, your velocity is 65 miles/hr or 29.1 m/sec. This
means that in 1 hr, you travel 65 miles or in 1 second, you travel 29.1
meters.
- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with
time. The units of acceleration are:
or meters per second per second (m/sec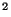 ). If you go from zero to 65
miles/hr (29.1 m/sec) in 10 seconds, your acceleration is 2.91
m/sec
). If you go from zero to 65
miles/hr (29.1 m/sec) in 10 seconds, your acceleration is 2.91
m/sec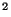 . Gravity causes objects to accelerate toward the center of
mass of planets or the Sun or other stars.
. Gravity causes objects to accelerate toward the center of
mass of planets or the Sun or other stars.
Ancient Astronomy
- The
Greeks, led by Aristotle & Ptolomy, envisioned an idealized universe
with the Earth at the center and all planets, the Sun, & the Moon
revolving around us in grand circles.
- The Greek astronomers preferred an Earth-centered or geocentric universe because of the lack of observed parallax of
the stars. Parallax is produced when a nearby object appears to move
relative to a distant background due to the motion of the observer.
- Interestingly, the planets were observed to undergo retrograde motion on occasion. Planets basically move west to east
relative to the stars, but occasionally will reverse direction and
travel east to west for weeks or even months. To explain this, the
Greeks resorted to the use of epicycles and deferents. This made for
complex motions and did not do a good job of predicting future
positions of planets.
About early history of science:
- Plato: 427 - 350 B.C.
- Socrates's pupil and close friend. Socrates was executed by Athens
(was forced to drink a fatal cup of hemlock. Reacting to shifting moral
values of his time, Plato searched for UNCHANGING standards. He turned
to the world of ideas (``Platonism''). The cause of the world coming
into being is the idea. The world is generated to fulfill the idea.
- Do not trust your feelings. Allegory of the Cave.
- Saving the phenomena
- Aristotle: 384-322 B.C
- Poetics: poetry - comedy and tragedy. Tragedy: six factors -
scenic presentation, lyrical song, diction, plot, character, thought.
- Look for the cause of things. ``Why'' is the main question.
- Final cause - purpose of an action.
- Motion: not just changing places, but more general as
fulfillment of Potential. (Growth of a plant, growth of a society ...).
- Every motion has its INTERNAL cause and purpose.
- Logic: reductio ad absurdum.
- Earth is a sphere in the center of the Universe.
- The universe does not change: everything is on circular motion.
- Ptolemy: Second century A.D., Alexandria. Author of Almagest
- Pythagoras: 585 - 495 B.C. The theorem. NUMBER. Beginning of Math.
- Ionian Cosmology (now Turkey and Greek Islands): search for fundamental
elements. Beginning of chemistry.
- What was difficult? ``To know thyself''.
- True philosopher pursues scientific inquiry for its own
sake; others demand that science pay in practical results.
- Ended in 494 B.C. : Persian invasion.
Copernicus: Beginning of a Revolution
- The problems & complexities of the geocentric model caused
Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543) to examine an alternative
sun-centered or heliocentric model of the solar system.
- His model proposed that:
- The Sun is at the center of the Universe.
- The distance between the Earth and the stars is much greater
than the Earth-Sun distance. This would explain the lack of
observed stellar parallax.
- The east to west daily motions of stars, planets, the Moon,
and the Sun are caused by the rotation of the Earth on its axis.
- The Earth and all the planets revolve around the Sun on circular
orbits. This produces the change in constellations observed from one
time of year to the next.
- Retrograde motion is an illusion caused by the fact that we
are observing other planets on the planet Earth which itself is
moving around the Sun.
- Although Copernicus' idea of a heliocentric solar system is
correct, his assumption of circular orbits made his model no
more accurate than that of Ptolemy. But, it had the beauty of
simplicity.
Implications of Heliocentric Model
- The Heliocentric Model offers additional explanations for some of
the basic observations of the sky and the Earth environment made for
thousands of years.
- Seasons:
- Seasons are produced by the fact that the Earth's rotation axis
is inclined by 23.5
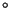 with respect to the line drawn
perpendicular to the Earth's orbital plane. Seasons are NOT produced
by the varying distance to the Sun as the Earth makes its elliptical
orbit about the Sun.
with respect to the line drawn
perpendicular to the Earth's orbital plane. Seasons are NOT produced
by the varying distance to the Sun as the Earth makes its elliptical
orbit about the Sun.
- The sunlight intensity (or amount of heating) depends on the angle
that the Sun's light rays make with respect to the ground. When the Sun
is highest in the sky at noon during the summer in Las Cruces, the Sun's
rays are nearly perpendicular to the ground - this produces the
greatest heating of the year. This is caused by the fact that the
northern hemisphere is pointing most directly at the Sun. The opposite
occurs during the winter.
- What other terrestrial planet has seasons?
- Eclipses
- Eclipses occur when one astronomical body moves into the shadow
cast by a second astronomical body.
- A Lunar Eclipse occurs at Full Moon when the Moon moves
through the shadow of the Earth.
- A Solar Eclipse occurs at New Moon when the Moon's shadow
falls upon the Earth.
- Question: Why isn't there a total solar eclipse at each New
Moon?
The Newtonian Universe
Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler
- Tycho Brahe's (1546-1601) precise observations of Mars set the
stage for Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) to make major modifications and
improvements on the heliocentric model.
- Kepler devised the following Laws of Planetary Motion:
- Law of Ellipses - The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with
the Sun at one focus. (Eccentricity of an ellipse is the ratio of
the distance between the focii divided by the length of the major
axis.)
- Law of Equal Areas - A hypothetical line drawn between a
planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.
In simpler terms, this means that a planet travels faster when it is
closer to the Sun.
- Harmonic Law - If
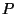 is a planet's orbital period around
the Sun (measured in Earth years) and
is a planet's orbital period around
the Sun (measured in Earth years) and 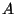 is the average distance
between the planet and the Sun (measured in AU), then
is the average distance
between the planet and the Sun (measured in AU), then
For example, if a planet had an orbital period of 8 yrs, then
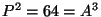 ; so A = 4 AU. So, by measuring the orbital period of a
planet through careful observations of the planet with respect
to the stars, one can determine its distance from the Sun.
; so A = 4 AU. So, by measuring the orbital period of a
planet through careful observations of the planet with respect
to the stars, one can determine its distance from the Sun.
- Kepler's laws are a correct description of planetary motion.
However, they lack any explanation as to why planets move in this
fashion.
Galileo: A Crisis in Conscience
- Galileo Galilei's (1564-1642) contribution to astronomy &
physics was immense as a result of his careful observations &
experiments. However, his beliefs in Copernican theory & his
great ego caused him much mental anguish at the hands of the
Inquisition.
- Among Galileo's best known accomplishments:
- He determined that the acceleration of falling objects was
independent of their mass.
- With his simple telescope, he was the first to observe that
Venus has phases. This proved that Venus must revolve around the
Sun & thus supports the heliocentric solar system.
- Galileo discovered the 4 brightest moons of Jupiter which
move around the planet like a mini solar system.
- Galileo discovered sunspots which violated Aristotle's view
that the Universe was perfect & unchanging.
Newton: A Revolution Completed
- Isaac Newton (1642-1727) was the first great theorist in
astronomy & physics. He invented calculus to provide the
framework in which to understand motions. He explained Galileo's
observations and Kepler's Laws using his theory of gravity.
- Newton's Laws of Motion:
- Law of Inertia - The natural state of an object is
either rest or motion in a straight line at constant velocity.
- Force Law - The change in an object's velocity must
be caused by a force. That force (
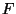 ) is given by
) is given by
where 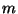 = mass and
= mass and 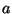 = acceleration. Whenever acceleration
is observed for an object, that object is subject to a force.
For example, an apple accelerates when it drops to the ground
implying that it is feeling a force - gravity.
= acceleration. Whenever acceleration
is observed for an object, that object is subject to a force.
For example, an apple accelerates when it drops to the ground
implying that it is feeling a force - gravity.
- Action/Reaction Law - For every applied force, a
force of equal magnitude but opposite direction arises.
- Newton's 3rd Law has several additional consequences:
- It is the basis behind the principle of Conservation
of Momentum. Momentum (
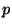 ) is defined as
) is defined as
where 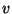 = velocity. When there are no other forces present,
the total momentum is a constant (or conserved). That is, if an
object, like a bullet, is shot from a gun (the action), the gun
will recoil (reaction) in the opposite direction. The gun recoil
is with slower speed than the bullet because its mass is
greater.
= velocity. When there are no other forces present,
the total momentum is a constant (or conserved). That is, if an
object, like a bullet, is shot from a gun (the action), the gun
will recoil (reaction) in the opposite direction. The gun recoil
is with slower speed than the bullet because its mass is
greater.
- The 3rd Law is the basis behind rocketry. The rocket
releases gas molecules (which each have low mass) at high speeds;
the rocket reacts by moving the opposite direction. This is true
for a launch off the Earth or for maneuvering in space.
The Law of Gravity
Gravity as a Mass Probe
- The mass of a planet can be determined by measuring how it
perturbs the motion of a smaller object such as an asteroid or a
spacecraft. Mercury's mass was determined by watching how the Mariner
10 spacecraft was accelerated as it approached Mercury. Similarly, the
orbit of Pluto's moon Charon was used to determine the mass of Pluto for
the first time during the last decade.
- Newton was able to derive Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion from
his own Laws of Motion and the Law of Gravity. In particular, he
generalized Kepler's 3rd Law and showed that it depended upon the mass
of 2 orbiting bodies as follows:
where 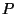 is the orbital period (in yrs),
is the orbital period (in yrs), 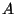 is the average distance between
the bodies (in AU), and
is the average distance between
the bodies (in AU), and 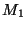 and
and 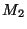 are the masses of the bodies
(in
are the masses of the bodies
(in 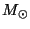 ). For our
solar system,
). For our
solar system, 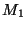 is the mass of the Sun (1
is the mass of the Sun (1 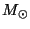 ) and
) and 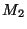 is the mass of a planet which is always much less than that of the
Sun.
is the mass of a planet which is always much less than that of the
Sun.
- This version of Kepler's 3rd Law can now be used for any situation
in which two objects are orbiting about each other (for example, a
binary star system) and can be used to determine the total mass of
the system (
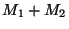 ).
For example,
the Galilean satellites orbit about Jupiter. We can measure the orbital
period by observing the motion of a Jovian moon over time and we can
measure the orbital radius (
).
For example,
the Galilean satellites orbit about Jupiter. We can measure the orbital
period by observing the motion of a Jovian moon over time and we can
measure the orbital radius (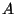 ) from a photograph. Then, plugging into
Newton's version of Kepler's third law above, we can determine the mass
of Jupiter (which is much larger than that of any of the moons,
) from a photograph. Then, plugging into
Newton's version of Kepler's third law above, we can determine the mass
of Jupiter (which is much larger than that of any of the moons,
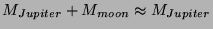 ).
).
Gravity in Action
Orbits & Spaceflight
- The orbiting of an artificial satellite or the Moon around
the Earth implies that there is a force present. Otherwise,
these objects would go flying off into space in a straight line
according to the Law of Inertia. The central force of gravity is
the key to holding these objects in their orbits.
- To place an object into orbit, the spacecraft must have
enough velocity along the orbit. Too little velocity and the
spacecraft will fall back to Earth. Too much velocity and the
object will escape into space. The exact orbital velocity needed
depends on the mass of the planet & the orbital altitude (Law of
Gravity equation).
- The above gives us guidance on how to go from one planet to
the next. To go to Mercury, a spacecraft must reduce its
velocity relative to that of the Earth going around the Sun so
that it can ``fall'' toward the center of the solar system. On the
other hand, the Galileo spacecraft heading toward Jupiter had to
increase its velocity to move outward away from the Sun.
- Why do astronauts appear to be ``weightless'' on the Space
Shuttle if gravity is present? This is an illusion. The Space
Shuttle is really free falling toward the Earth constantly but because
of its orbital speed, it misses the edge of the Earth. Any
free-falling objects appear to be weightless (person dropped from an
airplane in an enclosed box) because both the object and the container
are falling at the same rate.
- Artificial gravity can be created in space using a large spinning
object like a wheel. Because of the Law of Inertia, such objects will
press up against the edge of the wheel and feel an effective force like
gravity.
The Rings of Saturn
- The rings of Saturn are a good example of gravity in action. The
rings are believed to be the remnants of the material from which Saturn
formed. The rings are relatively thin - less than 5 km in width;
this flattening was caused by the rapid circular motion of the rings.
The rings are actually made of rocky material covered with ice that
range in size from small stones to a small car.
- Each rock in the ring follows an orbit around Saturn obeying
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion. So, you can predict the orbits of the
rings.
The Discoveries of Neptune and Pluto
- Neptune was discovered in 1846 as a direct consequence of
Newton's Law of Gravity.
- Following the visual discovery of Uranus in 1781 by William
Herschel, further observations of Uranus showed that it did not exactly
follow the predicted path. How could this be?
- The only way the orbit of Uranus could be perturbed would be by
another massive object (a planet) which was outside the orbit of
Uranus. If massive enough, it would exert a gravitational pull on
Uranus & cause its orbit to be slightly distorted.
- Using Newton's laws of gravity & motion, one can work backward
from the orbital perturbations to predict approximately the mass and
orbit of the mystery planet. Observers used these predicted positions
to discover Neptune in the middle of the last century.
- A similar prediction about the perturbation of the orbit of
Neptune led Clyde Tombaugh to search for & eventually discover the
planet Pluto. Pluto, however, turned out to be much less massive than
predicted. Also, we know today that the supposed perturbations in Neptune's
orbit do not exist. So, Pluto's discovery was pure serendipity.
Comets: From Fear to Triumph
- Comets were much feared by peoples of ancient times & the
Middle Ages. They were thought to forecast ominous events. For
example, one of the earliest recordings of Halley's comet in 1066
coincided with the conquest of England by the Normans - not good for
the Saxons!
- However, Halley's comet became a great triumph for
Newton's theories. Edmond Halley used Newton's newly developed theories
to predict the orbit of what came to be known as Halley's Comet. He
predicted that it would reappear every 75 years which was confirmed on
its passage near the Earth in 1758.
- Comets are on highly elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus.
They spend most of their time far beyond the orbit of Pluto. An entire
collection of proto-comets are believed to exist in a halo surrounding
the solar system at about 50,000 AU from the Sun - the Oort
Cloud.
- Comets are best described as dirty icebergs. The tail is
the most spectacular part of the comet - it can
be millions of kilometers in length. It is composed of gas molecules
which are left behind marking a trail of the comet nucleus.
- Some individuals have speculated that a giant comet or comets
struck the Earth 65 million yrs ago & was responsible for the death of
the dinosaurs in the Tertiary/Cretaceous period.
PART II - MATTER.
The Milky Way Galaxy
The Structure of the Milky Way
- The Milky Way galaxy consists of 3 parts:
- The Bulge is the center of our Galaxy. It is
densely packed with stars.
- The Disk is a flattened plane of stars, gas, and dust which
rotates about the center of the Galaxy.
- The Halo is a spherical cloud of thinly scattered stars and
Globular (star) Clusters.
- The Earth lies about 2/3rds of the way out from the galactic
center (8.5 kpc or 28,000 ly).
Stars & Star Clusters
- The Milky Way contains several hundred billion stars. Some are
bigger & brighter, and many are smaller & less luminous than the Sun.
- More than half of the stars in our Galaxy are double or binary stars. The closest star system, Alpha Centauri, is a triple
system.
- Possibly all stars in the galactic Disk are
born in galactic star clusters.
- The distance between stars is very large in our stellar
neighborhood. Alpha Centauri is 4.2 ly away. The density of stars
like the Sun is quite low. The Milky Way
galaxy is mainly empty space!
- Stars, like people, go through a life cycle: they are born, live
steadily through most of their lives, and then die.
The Interstellar Medium
- The space between stars is not totally empty. It contains gas and
dust but with a very low density - about 1 atom/cm
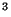 (compared to
(compared to
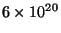 atoms/cm
atoms/cm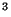 for the Earth's atmosphere). This is the
interstellar medium (ISM).
for the Earth's atmosphere). This is the
interstellar medium (ISM).
- Occasionally, gas gathers into larger & somewhat denser clumps
called nebulae. These gas clouds are often red in color.
These nebulae house stellar nurseries.
- The ISM contains mainly hydrogen gas.
- The ISM also contains significant dust which dims the light of
the stars that lie behind the dust clouds.
The Universe of Galaxies
Individual Galaxies
- There are a variety of galaxy types in the Universe:
- Spiral galaxies rotate, have a relatively cool ISM, and
are like our own Milky Way.
- Elliptical galaxies are somewhat shaped like a football,
do not have spiral arms, do not rotate, and have a hot (
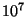 K)
ISM.
K)
ISM.
- Irregular galaxies have no organized shape, no symmetry,
contain young stars and much gas.
Groups and Clusters of Galaxies
- Most, if not all, galaxies are in groups or clusters.
- Our galaxy and about 22 others are part of the Local Group
of Galaxies. It is about 10 million ly in diameter.
- There are some truly gigantic rich clusters
which contain about 1000 galaxies and are more than 20
million ly in diameter.
The Expanding Universe
- In 1929, Edwin Hubble discovered that the Universe is expanding.
All galaxies are rushing away from all other galaxies.
- On very large scales the Universe is homogeneous
Gravity in Action II:
Binary Stars
- Binary stars revolve around each other and around a central
point called the center of mass. This is a kind of balance
point between the stars. The center of mass is closer to the
more massive star. (For our solar system, the center of mass is
actually inside the Sun since the Sun has 99% of the mass of the
solar system.)
- Binary stars are fundamentally important to astronomy because they
are the only way that we can directly measure the mass of stars. This
is done using Newton's version of Kepler's 3rd Law - we measure the
orbital period,
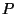 , and the average separation between the stars,
, and the average separation between the stars, 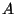 ,
and this gives us the sum of the masses of the stars in the binary
system.
,
and this gives us the sum of the masses of the stars in the binary
system.
- From these masses, astronomers find a tight relationship between
the mass and the luminosity of a star where luminosity is the
total energy radiating from a star per second (Watts). This means that
more massive stars radiate more energy than less massive stars.
Galactic Rotation & Dark Matter
- The Sun revolves around the center of the Milky Way galaxy with a
speed of 200-300 km/sec. It takes the Sun 200,000,000 yrs to make one
orbit around the Galaxy. The Sun revolves around the Galactic Center in
response to the gravitational pull of the hundreds of billions of stars
that lie interior to the Sun's orbit.
- In the outer parts of the Galaxy, astronomers expected the orbital
speed to drop off with distance since the mass interior to the orbit was
not expected to increase.
Much to our surprise, it was discovered about 18 yrs ago that the
rotation velocity remains constant out at large distances and does not decrease
as expected. What is happening here?
- The best
explanation for these higher than expected velocities is that the
mass is not decreasing as expected. But, since not many stars are seen
in the outer part of the Milky Way, this implies that the matter must be
dark or non-luminous.
- What is the nature of this dark matter? We really don't yet know.
It might be burned out stars, brown dwarf stars, Jupiter-like planets,
black holes or possibly exotic high energy particles which only weakly
interact with normal (like us) matter. Something to ponder - the
rotation velocities imply that there may be 10 times more dark matter than
luminous, so we may be the abnormal matter!
Clusters of Galaxies
- Clusters of galaxies can contain a few galaxies (like the Local
Group) or thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity. They are
the galaxy analog of the star clusters discussed above. Gravity keeps
the galaxies within the clusters and stops them from flying off into
space.
- In the 1930's, Fritz Zwicky discovered that there does not
appear to be enough luminous matter (stars) within the cluster
galaxies to keep the clusters together. To prevent such clusters from
flying apart, there must be substantial amounts of dark matter present
within the clusters as well.
- More recently, substantial amounts of X-ray emission have been
detected & imaged in clusters. This is very hot gas (
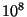 K)
that lies between the galaxies. To keep this hot gas bound to the
clusters, again there must be about a factor of 10 more dark matter
than luminous matter in clusters of galaxies.
K)
that lies between the galaxies. To keep this hot gas bound to the
clusters, again there must be about a factor of 10 more dark matter
than luminous matter in clusters of galaxies.
Summary
- All objects with mass attract all other objects with mass. Mass
is the driver behind gravity.
- Because gravity is a force, it causes smaller mass objects like
moons and satellites to accelerate when they encounter larger mass
objects. By observing the motion of such objects, we can calculate
the mass of the planet or star which is responsible for the
gravitational attraction using Newton's Law of Gravity or Kepler's 3rd
Law of Planetary Motion.
- Gravitational force also rapidly diminishes with distance. The
force of gravity decreases as
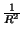 where
where 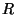 is the distance.
The closer you are to a planet or star, the stronger the force and the
more energy is required to escape.
is the distance.
The closer you are to a planet or star, the stronger the force and the
more energy is required to escape.
The Properties of Matter
Structure of the Atom
- Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. Their
structure and arrangement will determine the chemical composition &
basic properties of an object (a human being vs. a house). Atoms are
also responsible for producing light & can strongly interact with
light. So by studying the spectra of light emitted by a star, we can
determine the atomic structure of the star & its basic properties.
- The Nucleus lies at the center of an atom. The diameter of a
hydrogen nucleus is about
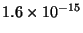 meters. The nucleus is
further composed of
meters. The nucleus is
further composed of
- Protons which are positively charged particles; and
- Neutrons which are uncharged particles.
- Electrons are tiny, small mass (0.05% of the proton
mass), negatively charged particles that orbit about the nucleus of
the atom. The electron charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in
sign to that of the proton.
- The electron is bound to the nucleus by an electric force which
acts somewhat like the gravitational force but is much stronger on small
scales. The strength of the electric force is proportional to
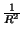 where R is the distance between the nucleus & the electron.
(Electrons at larger distances from the nucleus are said to be less
tightly ``bound'' to the atom since the electric force is weaker than for
a nearby electron.) However, for the electric force, opposite charges
attract and like charges repel.
where R is the distance between the nucleus & the electron.
(Electrons at larger distances from the nucleus are said to be less
tightly ``bound'' to the atom since the electric force is weaker than for
a nearby electron.) However, for the electric force, opposite charges
attract and like charges repel.
- When an electron is removed from a atom (as a result of a collision
with another atom, for example), the atom becomes ionized.
- The main difference between various chemical elements is the number
of protons, neutrons, and electrons that each atom of the element
possesses. Hydrogen has 1 proton, no neutrons, & 1 electron. Helium
has 2 protons, 2 neutrons, and 2 electrons. Uranium has 92 protons, 146
neutrons, & 92 electrons. Also, the distances from the nucleus and the
energies of electrons in each atom are different from all other atoms.
Temperature & Pressure
- Temperature is a measure of the speed of motions of atoms
or molecules in a gas. The faster the motion of the atoms/molecules,
the higher the gas temperature.
Two temperature scales are commonly used in science as follows:
- The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling
points of water. That is,
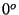 C corresponds to the freezing point
and
C corresponds to the freezing point
and 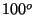 C corresponds to the boiling point of water.
C corresponds to the boiling point of water.
- The Kelvin scale is based upon the absolute zero point
where the velocity of gas atoms or molecules would be zero. That is,
0 K corresponds to
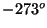 C. The relationship between the Celsius
and Kelvin scales is then
C. The relationship between the Celsius
and Kelvin scales is then
- Pressure is defined as force per area. For a gas enclosed
in a container, the gas pressure is a measure of how many atoms hit the
walls of the container and at what speed. It is related to density and
temperature as follows:
where 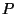 is the pressure,
is the pressure, 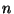 is the density,
is the density, 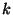 is a constant, and
is a constant, and 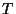 is the temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the atoms
will be moving and so these atoms will hit the container walls more often
thus increasing the pressure. Similarly, the larger the number of atoms
in the volume of the container (density), the more often the container
will feel the ``push'' from an atom striking a wall and thus increases
the pressure.
is the temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the atoms
will be moving and so these atoms will hit the container walls more often
thus increasing the pressure. Similarly, the larger the number of atoms
in the volume of the container (density), the more often the container
will feel the ``push'' from an atom striking a wall and thus increases
the pressure.
Molecules
- A molecule is a bonding together of 2 or more atoms.
Common examples are molecular hydrogen (
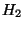 ), which is found in the
atmosphere of Jupiter & cooler stars; carbon dioxide (
), which is found in the
atmosphere of Jupiter & cooler stars; carbon dioxide (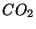 ), which
dominates the atmospheres of Venus & Mars; and ammonia (
), which
dominates the atmospheres of Venus & Mars; and ammonia (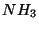 ) which
is an important constituent in the atmospheres of Jupiter & Saturn.
) which
is an important constituent in the atmospheres of Jupiter & Saturn.
- The abundance of a particular molecule is dependent upon the
temperature and pressure. High temperatures lead to more collisions
between molecules which can cause them to dissociate or break-up
into individual atoms. So, molecules tend to be found in cooler
environments like planetary atmospheres and interstellar clouds, and
not at the cores of stars or on the surface of the Sun.
Macroscopic States of Matter
- Matter in the Universe is found in three states:
- A solid usually has the highest density. Examples include the
surfaces of planets, asteroids, and neutron stars.
- A liquid usually has an intermediate density. Examples include the
Earth's ocean, a possible methane ocean on Titan (a moon of Saturn), and
the liquid metallic cores of the Earth & Jupiter which are responsible
for generating the planetary magnetic fields.
- A gas is usually the lowest density state. Examples include the
atmospheres of the planets, stars, the interstellar medium, and the
intergalactic medium. It is the most common state of matter in the
Universe.
- The particular state of matter of a given chemical composition
depends critically upon its temperature and pressure. For example,
water takes less time to boil at higher elevations; this is because
the boiling point of water is lower when the atmospheric pressure is
lower. Similarly, some states of matter cannot even exist if the
pressure is too low; this is true for the Moon and Mars where water
can only exist in either the frozen (ice) state or the gaseous state.
- The electrical properties of matter can also depend upon the
temperature & pressure. Even though the temperature is high near the
center of Jupiter, hydrogen has a liquid state which has electrical
properties like that of a metal.
Applications
Planetary Atmospheres
- The density and composition of the atmosphere of a planet
depends critically upon the temperature and mass (gravity) of the
planet. These effects produce atmospheres which range from a high
vacuum on Mercury to the thick atmosphere of Jupiter.
- The concept of escape velocity is important in
understanding planetary atmospheres. Remember that the force of
gravity holding us to a planet depends directly upon the mass of the
planet. The larger the mass, the higher the velocity or kinetic
(motion) energy necessary to escape from the planet. For small
planets like Mercury or satellites like the Moon, the gravitational
force is low and so is the escape velocity. Atoms & molecules do not
have to move very fast to escape from these bodies; such small planets
as Mercury do not retain their atmospheres whereas massive planets
like Jupiter are able to keep virtually all their original atmosphere.
Similarly, this is why Earth's atmosphere is denser and has a higher
pressure than Mars' atmosphere (because Mars' mass is only 11% that
of Earth).
- A second effect on planetary atmospheres is the temperature of
the planet. The higher the temperature, the faster the atoms &
molecules in the atmosphere move. Fast moving atoms mean that many of
them will achieve escape velocity and will leave the planet. This
effect is important on Mercury where the high temperature further
helped the atmosphere to escape whereas the cold temperatures near
Jupiter mean that the atoms & molecules rarely achieve escape
velocity.
- A third effect on atmospheric composition is the mass of the
atom or molecule. In a gas of a given temperature, lower mass atoms
will move more rapidly than higher mass atoms. So, lighter atoms will
be closer to the escape velocity than heavier atoms. Therefore, more
lower mass atoms will be lost from a planet's atmosphere than higher
mass atoms. This is why the Earth's atmosphere contains little
hydrogen but more heavy molecules & atoms (like nitrogen & oxygen),
whereas the massive Jupiter (& the Sun) is composed mainly of
hydrogen since the escape velocity is high.
- Our technology has advanced to the state where humans can
significantly affect and alter the atmosphere of Earth. Two
developments are of concern:
- The increased levels of
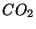 in the atmosphere produced by
industry, aircraft, etc. has led to a warming of the atmosphere,
termed the Greenhouse Effect, according to some scientists. The
in the atmosphere produced by
industry, aircraft, etc. has led to a warming of the atmosphere,
termed the Greenhouse Effect, according to some scientists. The
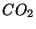 traps heat (infrared radiation) near the Earth's surface & can
cause the average temperature of the planet to rise. Potentially,
this can have catastrophic effects (melting of polar ice caps
producing coastal erosion; crop failures). Venus is an example of a
planet with a Runaway Greenhouse Effect that developed naturally as a
result of early outgasing of carbon & oxygen into the atmosphere; the
surface temperature is 700 K! There is a lesson to be learned here.
traps heat (infrared radiation) near the Earth's surface & can
cause the average temperature of the planet to rise. Potentially,
this can have catastrophic effects (melting of polar ice caps
producing coastal erosion; crop failures). Venus is an example of a
planet with a Runaway Greenhouse Effect that developed naturally as a
result of early outgasing of carbon & oxygen into the atmosphere; the
surface temperature is 700 K! There is a lesson to be learned here.
- Another potential human-made problem is the ozone hole. Ozone
is a molecule consisting of 3 atoms of oxygen. Ozone absorbs
ultraviolet radiation in our atmosphere. However, chlorofluorocarbons
from spray cans, jet engine exhaust, etc. are slowly breaking down the
ozone layer, especially over the Antarctic. Further erosion of the
ozone layer would permit more ultraviolet light onto the Earth's
surface which would lead to an increase in skin cancer and to crop
failures.
- On the positive side, human technology may allow us to someday
``terraform'' other planets like Mars - that is, to increase the
atmospheric density & pressure, thus allowing humans to breathe the
Martian atmosphere & allowing liquid water to again run on Mars'
surface.
Powering a Star
- Astronomers were puzzled for many years by how stars like the Sun
produce their energy. Do they burn coal at their core? (No, this is not
efficient enough.) Is the Sun continually contracting, heating up, &
then radiating this heat into space? (No, the Sun's lifetime of 5 billion
yrs is too long.) What is the macroscopic state of this matter?
The answer came with an understanding of nuclear
reactions in the middle of this century.
- The energy generation process in the core of the Sun is called
the p-p or proton-proton chain. Protons are converted into
helium, and in the process light energy is given off. In particular,
where 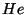 is a helium nucleus and
is a helium nucleus and 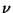 is a very low mass, neutral
particle called a neutrino. The protons must come together at very high
speeds (& so high temperature like that at the Sun's core,
is a very low mass, neutral
particle called a neutrino. The protons must come together at very high
speeds (& so high temperature like that at the Sun's core,
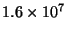 K) in a high density region so the protons will fuse together.
This kind of nuclear reaction is called fusion.
K) in a high density region so the protons will fuse together.
This kind of nuclear reaction is called fusion.
- The key to energy production in fusion is to recognize that the
mass of the helium nucleus is less than that of the 4 protons. Where
does the extra mass go? Einstein told us in 1916 that energy & mass are
equivalent such that mass can be converted into energy, and energy can be
turned into mass via
where 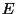 is the energy (light),
is the energy (light), 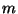 is the difference in mass between
the helium nucleus & the 4 protons, and
is the difference in mass between
the helium nucleus & the 4 protons, and 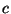 is the speed of light.
is the speed of light.
Dead Stars
- An interesting example of an extreme state of matter can be
found in dead stars. These are stars that have burned all their
hydrogen fuel at their cores and then gravitationally collapsed to a
small size but very high density. The very high pressure within these
stars produces very exotic states of matter.
- At the end of its lifetime in another 5 billion yrs, the Sun
will become a white dwarf star.
- White Dwarfs have a size less than that of the Earth but a
density of 1,000,000 gm/cm
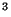 or a million times the density of
water! When a star like the Sun stops burning its nuclear fuel, there
is no longer any thermal pressure to resist gravity. So, the star
collapses under its own weight.
or a million times the density of
water! When a star like the Sun stops burning its nuclear fuel, there
is no longer any thermal pressure to resist gravity. So, the star
collapses under its own weight.
- Such stars are very hot on their surfaces (about 15,000 K vs.
6000 K for the current Sun) and emit most of their energy just by
cooling down. The stars became hot when they collapsed much like the
frictional heating when you rub your hands together.
- The core of a white dwarf is made almost entirely of carbon - a
kind of carbon crystal.
- White dwarfs have been observed in a number of cases. The most
famous is the companion of the luminous star Sirius, which is one of
the brightest objects in the night sky.
- Neutron Stars possess an even more exotic type of matter -
a star made up entirely of neutrons.
PART III - LIGHT
The Wave Nature of Light
- Unlike other branches of science, astronomers cannot touch or do
field work on their samples. The only information that we have is from
the light that is imaged by our telescopes. Fortunately, light
contains a wealth of physical information about the Universe.
- Light can be viewed as a traveling wave (like an ocean
wave). It is made up of electric & magnetic fields so light is
referred to as electromagnetic radiation.
- The wavelength is the distance between wave crests (units
are length). For optical light, a shorthand notation of angstroms (Å ) is used such that 1 Å
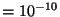 meters. So,
visible wavelength light is about 5000 Å.
meters. So,
visible wavelength light is about 5000 Å.
- The frequency is the number of wave crests that pass by a
detector per second of time. The units are Hertz (Hz), where 1
Hz is 1 cycle/sec. A typical radio frequency is 100 MHz (where MHz is
a million Hz).
- Light travels very fast at
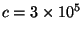 km/sec. This speed
is constant throughout space for all wavelengths.
km/sec. This speed
is constant throughout space for all wavelengths.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- In the visible, the rainbow of colors make up the spectrum. Color is the same as wavelength. Blue light has the shortest wavelength
and red light has the longest.
- The only difference between various parts of the electromagnetic
spectrum (such as radio and x-rays) is the wavelength. In order of
increasing wavelength: gamma-rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible,
infrared, and radio. Gamma-rays have wavelengths
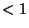 Å and radio
waves have wavelengths of meters.
Å and radio
waves have wavelengths of meters.
- The atmosphere is mostly opaque to the electromagnetic spectrum.
Only visible and radio waves easily penetrate the atmosphere with a
bit of ultraviolet & infrared as well. This means ground-based
telescopes operate in the visible & the radio, whereas space-based
telescopes (above the atmosphere) function at other wavelengths.
The Doppler Effect
- The Doppler Effect is the shift of the wavelength of light
produced by motion of an object toward or away from us. We experience a
similar effect with sound when a train approaches us & then moves away
from us - the pitch or the wavelength of the sound changes.
- The change in the wavelength between that
observed for a moving object and that measured when the light source is
at rest is directly
proportional to the wavelength. For stars moving away from us, the
wavelength change is toward the red and is called a redshift. For
stars moving toward us, it is a blueshift.
- The Doppler Effect provides astronomers with a powerful tool for
measuring radial velocities of planets, stars, & galaxies. All we need
to do is measure the difference between the observed wavelength
and the wavelength measured in the laboratory.
The Inverse Square Law
- When we look at the night sky, we see that all stars are not the
same color or brightness. Brightness is the amount of energy
per second per area that falls on a detector such as a photographic
plate or on the retina of our eyes. Brightness depends upon two
factors:
- The total energy per second or luminosity emitted by a
star or other object. For example, a 200 Watt light bulb appears
brighter than a 100 Watt light bulb if they are side by side.
- The distance of the light source from the observer. The further
away the light source, the less bright it appears.
- This dependence of brightness upon distance is called the Inverse Square Law. Once again, it is very much like the Gravity
Force Law in that the brightness of a light source is proportional to
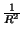 , where R is the distance between the light source and the
observer.
, where R is the distance between the light source and the
observer.
- So, when we look at a star, it may be faint because it is far
away or it is low luminosity or a combination of the two.
Kirchhoff's Laws of Spectral Analysis
- To understand how stars and galaxies function, we must first
understand how such objects produce the light that we observe with our
telescopes - light is the only information that we can sample from
most astronomical objects.
- In the last century, Gustav Kirchhoff (1824-1887) formulated 3
rules or laws which govern how light is produced by various states of
matter. He stated that:
- A dense, hot substance produces a continuous spectrum with
all the rainbow colors. An example is a fireplace poker or the
filament of a light bulb.
- A low density, hot gas emits bright emission lines. An
example is the gas around new stars like the Orion nebula.
- If a continuous spectrum passes through a gas at a lower
temperature, the cooler gas produces dark absorption lines.
- The Challenge: Explain these interesting rules for the
production of light using our knowledge of matter.
Continuous Emission & Blackbody Radiation
- Notice that a fireplace poker starts off looking a dull red then
a brighter red and finally is blue-white hot as we increase the
temperature of the metal. An object like this whose light emission
properties depend only upon temperature is called a blackbody.
It is a perfect radiator of energy. As a blackbody heats up, it
begins to radiate away its energy as light, first starting off with
most of its emission in the infrared then in the visible and finally
in the ultraviolet. Stars are good approximations of blackbodies.
- A blackbody emits continuous radiation and meets the conditions
outlined by Kirchhoff. The properties of a blackbody include:
- The electromagnetic radiation from a blackbody is strongly
peaked at a particular wavelength that depends only on the temperature
of the blackbody. A hot blackbody will appear to be blue and a cool
blackbody will appear to be red. So, by just looking at the color of
a star, you can get a pretty good idea of its temperature! A yellow
star like the Sun has a temperature of 5500 K, whereas a red star like
Betelgeuse has a temperature of only 3000 K.
- A blackbody emits some radiation at all wavelengths.
- The energy per area radiated by a blackbody will increase with
temperature. In other words, for two stars at the same distance with the
same radii, the star with the highest temperature will appear to be
the brightest.
Spectral Lines & the Bohr Model
- The German physicist Max Planck proposed in
the late 1800's that light can be viewed as both a wave and a massless
particle. The light particle or quanta is called a photon.
Each photon carries both momentum and energy. The photon energy
directly increases with frequency so gamma-ray photons have more
energy than infrared photons.
- Neils Bohr in the early part of this century first correctly
described a working model for the hydrogen atom. He hypothesized that
electrons can only occupy certain orbits at selected distances from the
nucleus. They cannot lie between these particular orbits.
Furthermore, each atom has a unique set of orbits which corresponds to
different orbital energies. So, the electron orbits are said to be quantized.
- The lowest orbit or energy level of an atom is called the ground state.
- When an electron is in some orbit above the ground state, it is
said to be excited.
- Next, Bohr recognized that when an electron jumps from a larger
radius (or higher energy level) orbit to a lower radius orbit, it must
give up energy. This energy is in the form of a photon which has
exactly the energy that corresponds to the difference in energy
between the two orbits. Such an electron transition produces an
emission line.
- In practice, an emission line can be produced as follows. A
gas, say around a young star, is heated by the energy radiated from
the new star. This higher temperature means that the atoms are moving
faster. When the atoms collide, some of their energy goes into
causing the electron to rise to a higher orbit or energy level. But,
electrons like to be in their ground state which is accomplished by
emitting a photon and thus giving up the energy gained via the
collision. Such gas around young stars produced what are called emission line nebulae.
- An absorption line is produced when an atom absorbs a photon and
the electron jumps to a higher orbit or energy level. It is important
to note that only photons with exactly the energy corresponding to the
difference in energy between the two electron orbits will be absorbed.
All other photons will be ignored. This is why only discrete
wavelengths will be missing from an absorption line spectrum. The
missing wavelengths correspond to the energy levels of particular
atoms. Since each atom has a unique set of orbits & energy levels,
the corresponding spectrum will be unique.
- With only the spectrum from a star, we can determine its
temperature and its chemical composition.
Further Thoughts on Light
The Sun
- The Sun's atmosphere has three layers:
- The photosphere is the layer that we see. It has a
temperature of about 5800 K.
- The chromosphere lies above the photosphere. Surprisingly,
it is hotter - up to a million degrees K.
- The corona is the outermost layer that extends out to
several solar radii. Its temperature is about 2 million degrees K.
- More about the photosphere:
- It has a characteristic temperature of 5800 K.
- Since this temperature is lower than that of the interior (which
is 16,000,000 K at the core), we have the classic situation described
by Kirchhoff for absorption lines. The Sun has an elaborate
absorption line system arising from most of the known elements.
Interestingly, helium was first detected on the Sun (via its
absorption lines) before it was discovered on Earth.
- The surface of the photosphere has a mottled appearance with a
pattern of light & dark structures known as granulation. This
granulation is the result of the heat rising from the interior to the
surface of the Sun much like a pot of boiling water. This type of
heat transport is called convection and occurs in stars with
masses similar to and less than that of the Sun.
- The surface of the Sun is not always peaceful, but can undergo
periods of activity which are related to the magnetic fields.
Astronomers can measure magnetic fields on
the Sun; in the presence of strong magnetic fields (8000 times that on
Earth), the energy levels in atoms will further divide. This means
that in the spectrum of a gas with a strong magnetic field, two lines
rather than one will appear. The separation of the line pair is
directly proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
- Activity on the Sun is manifested in several ways:
- Sunspots are dark, cooler regions on the Sun's surface.
These are regions with enhanced magnetic field. The magnetic field
pressure holds back some of the hot gas rising from the interior to
make the sunspots cooler. Sunspots usually come in pairs where one
sunspot corresponds to the magnetic north pole & the other to the
south pole where field lines stretch between them. The period between
sunspot maxima (when there is the largest number of sunspots) is 11 yr
and this appears to be related to the time needed for the Sun's
overall magnetic field to become tangled and untangled.
- Solar prominences are loops of hydrogen gas that rise
above the solar surface. They usually appear near sunspot groups and
appear to trace out magnetic field lines going from a north to a south
magnetic pole.
- Solar flares are very energetic streams of protons,
electrons, and ions which leave the Sun in bursts. They produce the
auroras on Earth and can also interfere with our communications. These
particles are energized in regions on the Sun where magnetic field
lines reconnect producing a burst of light, radio emission, X-rays,
and gamma-rays in addition to these energetic particles.
- Coronal holes appear in the outermost layer of the sun and
were discovered by the Skylab mission in the mid-1970's using X-ray
sensitive film. Because the corona has a temperature of about
1,000,000 K, it's blackbody spectrum peaks in the X-ray. Holes were
detected in this coronal X-ray emission which appear to coincide with
regions where magnetic field is streaming outward from the Sun (and
not immediately looping back) and carrying gas away with it.
The Interstellar Medium
- Recall that the distance between stars is very large. But, this
space is not empty. It is filled with a gas that has an average
density of 1 atom/cm
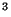 called the interstellar medium (ISM).
The temperature of the ISM varies from very cold (10 K) at the centers
of molecular clouds to
called the interstellar medium (ISM).
The temperature of the ISM varies from very cold (10 K) at the centers
of molecular clouds to 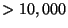 K near young stars.
K near young stars.
- Emission lines originate from the hot gas around young stars.
As new
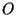 and
and 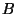 stars ``turn on'', the
ultraviolet light from these stars heats the gas and ionizes the
hydrogen atoms in the surrounding nebula. When these free electrons
collide with the ionized hydrogen atoms, they recombine and the
electrons cascade back down through the energy levels emitting light
at discrete wavelengths. Such Emission Line Nebulae
appear red in color because of the abundance of red wavelength emission
lines on visible wavelength images. Emission Nebulae are seen in both the
Milky Way (example: the Orion Nebula) and in the spiral arms of other
galaxies - anywhere that young, hot stars are being born.
stars ``turn on'', the
ultraviolet light from these stars heats the gas and ionizes the
hydrogen atoms in the surrounding nebula. When these free electrons
collide with the ionized hydrogen atoms, they recombine and the
electrons cascade back down through the energy levels emitting light
at discrete wavelengths. Such Emission Line Nebulae
appear red in color because of the abundance of red wavelength emission
lines on visible wavelength images. Emission Nebulae are seen in both the
Milky Way (example: the Orion Nebula) and in the spiral arms of other
galaxies - anywhere that young, hot stars are being born.
- Even the neutral hydrogen gas that is away from young stars can
produce emission line radiation, but in the radio part of the
spectrum. This spectral line has a wavelength of 21 cm. It was
discovered first in the early 1950's by groups in the U.S. & the
Netherlands. The 21 cm line is produced by a spin-flip
transition even though the atom is in its ground state. That is,
both the electron & the proton in the atom are spinning. The very
lowest energy state is when they are spinning in opposite directions.
A transition from parallel spins to anti-parallel spins produces a 21
cm spectral line.
- In dense (
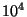 atoms/cm
atoms/cm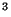 ), cold (10 K) clouds (where stars
have not yet ignited), molecules are abundant. They, too, can emit
spectral lines particularly in the IR and radio. Molecules such as
), cold (10 K) clouds (where stars
have not yet ignited), molecules are abundant. They, too, can emit
spectral lines particularly in the IR and radio. Molecules such as
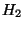 , OH, CO, and even
, OH, CO, and even 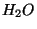 are observed.
are observed.
- Dust is the final important ingredient in the ISM. It
does three things to observations of distant stars in the visible:
- Dust dims light. This is called interstellar extinction.
This will tend to make stars look further away than they actually are,
so we need to be careful to correct for this effect.
- Dust reddens light as a result of preferentially scattering blue
light; that is, more red light makes it through a dust cloud while
blue light is scattered in many directions. This is the same effect
that produces red sunsets on Earth.
- Reflection Nebulae are the result of dust scattering; these
nebulae appear to be blue in color because the blue light has
been scattered into our line of sight. Such reflection nebulae
``shine'' by reflected starlight.
PART IV - ORIGINS
Star Formation & Evolution
Stellar Classification
The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram
- An extremely useful tool for understanding the evolution of a
star is the H-R diagram first devised in the early part of the
century. It is a plot of stellar temperature (or spectral class) on
the horizontal axis versus stellar luminosity
on the vertical axis. It was found that particular types of stars lie
on certain regions in this diagram according to their evolutionary
state and their mass.
- Regions on the Diagram:
- The Main Sequence runs from the top left to the bottom
right in the H-R diagram. These are all ``ordinary'' stars, which
like the Sun, are burning nuclear fuel at their centers. Stars in the
upper left are luminous & have very high temperature; from the
mass-luminosity relationship, we also know that these are the most
massive main sequence stars. Stars in the lower right are low of
luminosity, cool, and have masses smaller than the Sun. Notice the
position of the Sun about mid-way on the Main Sequence.
- Giant & Supergiant stars lie in the upper right hand
portion of the H-R diagram. These stars are luminous but have cool
outer envelopes. According to our knowledge of blackbodies, a star
which is cool can only be luminous if it has a large surface area
(and, therefore, large radius) from which energy is emitted; thus,
their position on this diagram requires such stars to be giants.
- Finally, the lower left portion of the H-R diagram contains white dwarfs. These stars are hot but relatively low luminosity.
Again, using the same reasoning for blackbodies, such a hot star will
have limited total energy emitted if it is small in radius.
Protostar Formation
- Gravity and energy are the keys to understanding star formation
& evolution.
- Gravity is constantly trying to pull matter toward the center of
mass of a gas cloud or a star.
- Since stars do not have an infinite supply of energy, they must
readjust their structure in response to the energy supply. Initially,
gravitational collapse is the only source of heat. Later, nuclear
reactions power a star; the thermal pressure from the heat at the core
balances gravity. When the nuclear energy is exhausted, the star's
structure must again change in response to the changing energy
balance.
- Stars begin as roughly spherical, cold (10 K) molecular clouds.
They probably are rotating very slowly. A shock wave (possibly from a
supernova) may be the stimulus which causes the gas cloud to begin to
collapse. The shock compresses the gas & makes it denser. Then, the
self-gravity of the cloud causes the gas to contract toward the center,
further increasing the density.
- Conservation of Angular Momentum plays an important role
in the evolution of a star-forming nebula. Angular Momentum (L) is
defined as:
where 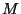 = mass of the cloud,
= mass of the cloud, 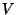 = rotational velocity of the cloud,
and
= rotational velocity of the cloud,
and 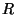 = cloud radius. For an isolated cloud, angular momentum must
be conserved (that is, remain constant) as the cloud gravitationally
collapses. But, for
= cloud radius. For an isolated cloud, angular momentum must
be conserved (that is, remain constant) as the cloud gravitationally
collapses. But, for 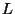 to be constant while
to be constant while 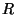 is decreasing (and
is decreasing (and
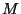 does not change),
does not change), 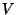 must increase; thus, the star must rotate
faster as it collapses.
must increase; thus, the star must rotate
faster as it collapses.
- Now, as the cloud continues to collapse, the center becomes
denser and hotter much like heat being generated when you rub your
hands together. At this point in time, the dense object at the core
of the gas cloud is called a protostar - an object not yet a
star, but it is one in the making.
``Turning On'' a Star
- The evolution of a protostar can be followed on the H-R diagram.
The early protostar is relatively cool and low luminosity (much of the
energy is radiated in the infrared). So, the star first appears on
the extreme lower right portion of the H-R diagram.
- The protostar's original free-fall contraction is slowed by the
increasing density and internal pressure at its center. The star
still is not hot enough to begin nuclear reactions so it must contract
further as it radiates energy from its surface.
- During its contraction phase, the protostar converts
gravitational energy into heat energy. Half the energy is radiated
into space and the other half goes to further raise the temperature of
the protostar's core.
- Finally, when the core is hot enough (about
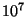 K for a 1
K for a 1
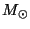 star), thermonuclear reactions begin. At this point, the
star enters onto the Main Sequence of the H-R diagram for the first
time. For a star like the Sun, it will remain on the Main Sequence
for about 10 billion yrs.
star), thermonuclear reactions begin. At this point, the
star enters onto the Main Sequence of the H-R diagram for the first
time. For a star like the Sun, it will remain on the Main Sequence
for about 10 billion yrs.
- While on the Main Sequence, stars are in pressure equilibrium.
That is, there is a balance between the force of gravity (directed
toward the star's center) and thermal (or heat) pressure caused by
energy released from the nuclear reactions in the core (directed
outward). During its life on the Main Sequence, the star neither
expands nor contracts.
How Do Different Mass Stars Evolve?
- The mass of a star has an important role in determining its
evolution. The larger the mass,
the more quickly the star will evolve onto and off of the Main
Sequence. A 1
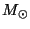 star takes about 30 million yrs to evolve
onto the Main Sequence, but a 15
star takes about 30 million yrs to evolve
onto the Main Sequence, but a 15 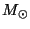 takes only about 160,000
yrs and a 0.2
takes only about 160,000
yrs and a 0.2 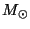 star takes about 1 billion yrs.
star takes about 1 billion yrs.
Evolution Off of the Main Sequence
- Massive stars consume their fuel quickly & live relatively
short lives on the Main Sequence whereas low mass stars conserve their
fuel & shine for billions of years. For example, a 25
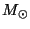 will live only 7 million yrs on the Main Sequence, whereas a
will live only 7 million yrs on the Main Sequence, whereas a 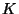 star
can continue to burn its nuclear fuel for 17 billion yrs.
star
can continue to burn its nuclear fuel for 17 billion yrs.
- Main Sequence stars ``shine'' by fusing hydrogen into helium.
When about 90% of that hydrogen has been exhausted, great changes
occur in the structure, luminosity, & size of the star. The star
begins to evolve off of the Main Sequence.
- Once the hydrogen in the core is depleted,
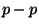 nuclear
reactions cease and the helium core begins to contract (thermal
pressure no longer can offset gravity). The core temperature begins
to rise. The larger core temperature results in the ignition of a
shell of hydrogen which surrounds the core.
nuclear
reactions cease and the helium core begins to contract (thermal
pressure no longer can offset gravity). The core temperature begins
to rise. The larger core temperature results in the ignition of a
shell of hydrogen which surrounds the core.
- The star moves toward the upper right portion of the H-R diagram
- the Giant Branch. The hydrogen shell burning has caused the
star's envelope or atmosphere to rapidly expand with the outermost
layers cooling due to the expansion. After another 5 billion yrs, our
Sun will become a Red Giant. A star can remain a Red Giant only
for about 10% of its total lifetime.
- Meanwhile, the helium core continues to contract & heat. Once
the core temperature reaches 100 million K, nuclear reactions begin
again. This time, three helium nuclei fuse to produce a carbon
nucleus in what's called the Triple Alpha process.
- For stars with masses of
 , subsequent contraction
and core heating can result in the production of even heavier nuclei
all the way up to iron in the core.
, subsequent contraction
and core heating can result in the production of even heavier nuclei
all the way up to iron in the core.
Star Death
- For a medium-mass star like the Sun, the triple-alpha process is
the last nuclear reaction in the core. Once the core has been
converted into carbon, the star begins to collapse again and becomes a
white dwarf, where degenerate gas pressure halts the collapse.
It moves to the lower left portion of the H-R diagram. As the white
dwarf radiates its energy into space, the star cools off and the
luminosity declines. Eventually the star becomes a cold & dark
carbon cinder called a black dwarf.
- For stars with mass
 , the end can be quite
spectacular. Such a star is layered like an onion with an iron core,
surrounded by a layer of silicon, then oxygen, then carbon, then
helium, and finally an outer ``skin'' of hydrogen. The evolution
then proceeds as follows:
, the end can be quite
spectacular. Such a star is layered like an onion with an iron core,
surrounded by a layer of silicon, then oxygen, then carbon, then
helium, and finally an outer ``skin'' of hydrogen. The evolution
then proceeds as follows:
- As the star develops an iron core, the energy production
declines (iron has a very tightly bound nucleus) and the core
contracts. As the core reaches 5 billion K, the photons have reached
gamma-ray energies which break up iron nuclei and cause the core to
collapse VERY rapidly.
- This rapid collapse triggers a star-destroying explosion called
a supernova. The contraction of the innermost degenerate core
allows the rest of the core to fall inward producing a huge shock (or
compression) which propagates outward and blows off the outer part of
the star. This explosion results in a rapid rise in luminosity,
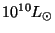 , for a brief period of time.
, for a brief period of time.
- The core collapse transforms iron to heavier nuclei, all the way
to the end of the periodic table. A supernova is the ONLY way that
elements heavier than iron can be produced in nature.
- The remaining core of the star may be either a neutron star
(which can produce a pulsar) or a black hole.
- Observations of supernovae have been recorded in historical
records in 1054 A.D. (now the Crab nebula), Kepler, etc. The most
recent, closest supernova was seen in 1987 in the Large Magellanic
Cloud. Spectra of supernova remnants have very wide line widths
indicating gas is moving outward at up to 10,000 km/sec!
Formation of the Solar System
Review of Solar System Properties
- Let's review the major properties of the solar system which must
be explained by a model of its formation.
- Dynamical Properties
- All planets revolve in a counterclockwise direction as seen
above the north pole of the solar system.
- Planetary orbits are nearly all in the same plane.
- Most moons revolve counterclockwise & near the planet's
equatorial plane.
- Orbits are nearly circular.
- Most planets rotate in a counterclockwise direction.
- Most of the angular momentum in the solar system is in the
orbital motion of the planets rather than the rotation of the Sun.
- Planetary rings are found around all the gas giant Jovian
planets.
- Chemical Properties
- Terrestrial Class - Silicon, iron, aluminum, and other
rocky materials which melt around 2000 K.
- Icy Class - carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, water, methane,
ammonia, etc. which melt at around 273 K (
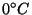 ).
).
- Solar Class - hydrogen, helium, neon, argon, etc. which
remains a gas down to around 10 K.
Table of Compositions of Objects by %
| Object |
Terrestrial |
Icy |
Solar |
| |
|
|
|
| Terrestrial Planets |
70% |
30% |
0% |
| Asteroids |
70% |
30% |
0% |
| Jupiter/Saturn |
1% |
10% |
89% |
| Uranus/Neptune |
10% |
80% |
10% |
| Comets |
15% |
85% |
0% |
The Nebular Model
- The Nebular Model for the formation of the solar system is an
extension of that proposed for star formation in general. The model
originated in the 1700's by Kant and LaPlace.
- Our solar system began from a roughly spherical gas cloud. The
cloud was enriched with heavy elements from a previous generation star
which exploded as a supernova - a crucial aspect for life as we know
it. The gravitational collapse was again stimulated by a shock wave.
- As the nebula contracted, it rotated faster according to the
Conservation of Momentum. This faster rotation also resulted in a
flattening of the gas cloud as expected by Newton's Law of Inertia.
Eventually, the cloud flattened into a relatively thin plane which
eventually formed the planets and the protosun was at the center.
- One major problem for this model is the distribution of angular
momentum in the solar system. With such a collapse, we would have
expected the Sun to be rotating more quickly and the planets revolving
more slowly than is observed. How was the angular momentum
transferred to the planets? The current model suggests that this was
done via magnetic fields while the solar system was still in a gaseous
state. Magnetic fields, which stretched from the protosun to the
outer nebula, acted to break the rotation of the Sun and to ``stir''
the outer nebula.
- Tiny dust grains formed when molecules
collected together, much like the growth of a
snow flake.
- Next, the dust grains began to stick together. These objects grew
to the size of large
boulders (up to a 100 km in diameter) called planetesimals which
probably resembled today's asteroids.
- These planetesimals collided to form protoplanets which
were the massive objects that eventually became planets. The most
massive protoplanets grew fastest since they had more gravity and
would attract even more mass.
- Finally, the planets cooled and atmospheres formed. In the case
of the terrestrial planets, surface evolution continued via meteoritic
cratering and erosion.
- Now, return to the list of solar system characteristics to see
how successful the Nebular Model is in explaining them.
Origin & Evolution of the Moon
Formation of the Moon
- Four major theories have been proposed for the formation of the
Moon:
- The Fission hypothesis proposed that the Moon broke away
from a rapidly spinning Earth. The problem is Moon rocks (from Apollo)
fundamentally differ from those on Earth.
- The Condensation hypothesis suggests that the Earth and
Moon condensed out of the same cloud of material in the solar nebula.
The problem is that the densities of the Earth & the Moon are quite
different.
- The Capture hypothesis suggests that the Moon was formed
elsewhere in the solar system & later gravitationally captured by the
Earth. This scenario has a very low probability.
- The Large-Impact hypothesis proposes that the Moon was
formed from the debris of an impact between a proto-Earth and a large
Mars-sized object.
- The Large-Impact hypothesis is currently favored because it
explains a number of observations. For example, a glancing collision
would have ``spun up'' the resulting material & would thus explain
the present angular momentum in the Earth-Moon system. A glancing
collision would also have ejected mainly lower density mantle material
which coalesced to form the Moon.
History of the Moon
- The first of four stages of evolution of the Moon involved
differentiation. Although the Moon is relatively poor in iron, what
was there sunk to the center and the low density material floated to
the top. The surface solidified 4.1-4.6 billion yrs ago.
- Intense cratering characterized the second stage. This formed
the large impact basins on the Moon.
- The third stage involved volcanic activity and lava flow.
Radioactive decay may have heated the subsurface layers to produce
volcanoes. The lava filled the impact basins and produced the Maria or darker regions which we can see on the Moon today.
- The final stage of on-going evolution is lower level impact
cratering which is caused by some remaining rocky debris falling onto
the lunar surface.
Galaxies & Galaxy Formation
Two Populations
- In the 1940's, W. Baade was the first to recognize two different
populations of stars in spiral galaxies which are today believed to be
understood within the spiral-density wave theory. They are:
- Population I stars are like the Sun. They are second
generation stars, rich in heavy elements, often blue in color, and are
found within spiral arms.
- Population II stars are older, previous generation stars.
They contain relatively little heavy elements, are red in color, and
are found in the galaxy halos (globular clusters), galactic nuclei,
and in the general disk. Few Pop II stars are found near the spiral
arms where active star formation is taking place. Also, Pop II stars
dominate elliptical galaxies.
- POPULATION I:
- Metal-rich young stars in disk
- H
 regions (hot gas around young stars
regions (hot gas around young stars
- Open clusters and stellar associations
- Cepheids (bright variable stars: period is 3-30 days
- POPULATION II:
- Old stars: metal-poor
- Globular clusters: 10 pc, 1 million stars
- RR-Lyrae stars
Galaxy Diversity
- An unresolved question in astronomy is how are the different
kinds of galaxies produced? Recall that the 3 basic galaxy types are
ellipticals, spirals, and irregulars. They have very different
characteristics:
- Spirals have prominent spiral arms in their disks; the disks
rotate about the galaxy centers; there are young stars in the disk;
there is an abundance of cool (
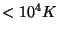 ) gas in the ISM.
) gas in the ISM.
- Ellipticals are not flattened into disks like spirals; there is
little or no organized rotation; there is no new star formation taking
place within ellipticals; the ISM is hot (
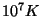 ) & emits X-rays.
) & emits X-rays.
- Irregulars are chaotic in appearance; there are young stars
within them; there is cool gas inside the ISM.
Interacting Galaxies
- The probability of galaxies interacting, especially in clusters,
is relatively high. In fact, it is more likely that 2 galaxies will
collide than 2 stars in the Milky Way. This is because the ratio of
the galaxy size to the average distance between galaxies is much
larger than a similar ratio for stars.
- When galaxies come near each other, the mutual gravitational
forces can tear stars & gas out of each galaxy. This can produce
very interesting ``tails" of stars & gas that stretch into
intergalactic space.
- Sometimes, galaxies can actually merge together. It has been
suggested that elliptical galaxies form as a result of mergers of
spiral galaxies. This has been demonstrated using computer modeling
called N-body simulations.
- Also, large galaxies at the cores of rich clusters may be formed
by ``galactic cannibalism" in which these large galaxies grow as a
result of digesting smaller galaxies that occasionally come close to
the cluster center.
- It is also likely that such galaxy interaction can trigger
activity within the nucleus of a galaxy resulting in the production of
extended radio sources. Such interaction causes gas to fall toward
the nucleus of galaxies which in turn may provide fuel to fire the
radio source ``engine".
Large Scale Structures in the Universe
- Groups of Galaxies: 2-20 galaxies, size=0.5 Mpc, 1/2 of all
galaxies belong to a group. Galaxies in groups are
mostly spiral galaxies and irregulars.
- Filaments: a dozen or more galaxies in a chain, mostly spirals
or irregulars, few Mpc long.
- Clusters: a thousand of galaxies, mostly ellipticals and
spirals with a very small amount of gas. There is hot gas between galaxies (100
million degrees). Galaxies move with very large velocities:
1000 km/s. Size of clusters:
1- 3 Mpc. Often there is a large central elliptical galaxy.
- Superclusters: Long (30-100 Mpc) very anisotropic
structures. Each supercluster includes many groups, filaments, and
few clusters.
- Voids: Large, almost empty areas. The same linear size as
for superclusters.
- The driving force behind the formation of galaxies and large
scale structures, such as superclusters, is gravity. Gravity
attracts matter into increasingly larger scales of structure.
- Supercomputer models are successful in reproducing the observed
distribution of structures on scales of hundreds of millions of light
years ONLY if the Universe is composed of at least 90% dark matter.
The exact form of this dark matter is not known at present
- Galaxies and larger structures begin as gaseous density
fluctuations in the early Universe. These regions are slightly denser
than the surrounding gas. Gravity causes them to collapse much like
the star-forming nebulae discussed earlier.
- In the early 1970's, the Russian astrophysicist Y. A. Zeldovich
proposed that large (a billion ly) clouds collapsed to form
pancake-like structures which became the filamentary superclusters
that we observe today. The empty regions left behind would produce
the cosmic voids.
The Formation of the Milky Way
- In many ways, spiral galaxies like the Milky Way are the most
complex and have the greatest diversity of properties. It is believed
that spiral galaxies begin as slowly rotating, giant, gas
clouds. Gravity causes the cloud to collapse. As in the case of the
solar system, the proto-galaxy cloud spins faster and flattens into a
disk as it collapses. This gives the Galaxy its organized rotation
and the thin galactic disk.
- As the Galaxy collapses, some of the gas fragments into smaller
clouds which become the sites for the first epoch of star formation.
These first generation stars are very massive (
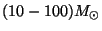 ), go
through their lifetime quickly, and explode as supernovae.
), go
through their lifetime quickly, and explode as supernovae.
- Galaxies form hierarchically: A small cloud forms. Then it collides
and merges with another small cloud. Then it collides and merges with even
bigger cloud, and so on.
- Spiral galaxies form in a process of multiple mergers with small
proto galaxies.
- Quick and violent merging produces an Elliptical galaxy.
How do the spiral arms form in galaxies like the Milky Way?
- The most popular idea since the 1950's is the spiral density wave
theory. It proposes that spiral shock waves rotate
about the galaxy.
- When gas clouds encounter the spiral density wave pattern, the
shock waves compress the gas and trigger star formation. This
explains why young
 &
&  stars, emission nebulae, and neutral
hydrogen clouds (radiating via 21-cm radio emission) serve to define spiral arms in
the Milky Way and other galaxies.
stars, emission nebulae, and neutral
hydrogen clouds (radiating via 21-cm radio emission) serve to define spiral arms in
the Milky Way and other galaxies.
- An important aspect of the Spiral-Density Wave theory is that
star-formation is an on-going activity within spiral galaxies. This
leads to multiple epochs of star formation - second or even third
generation stars like our Sun which are enriched with heavier
elements.
Black Holes & The Theory of Relativity
Overview of Relativity
- By the beginning of the 20th century, it became clear that
Newton's Laws of Motion & Gravity were not completely general. In
particular, Newton's Laws do not correctly describe motions of objects
that are traveling near the speed of light or that are in a very
strong gravitational field.
- Einstein developed several important postulates about motion:
- There is no absolute rest frame in the Universe. The best that
one can do is measure relative motions.
- The speed of light,
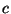 , is constant with respect to all
observers, independent of velocity. This makes light a very different
phenomenon from objects with mass that have different apparent
velocities depending on the motion of the observer. This result gives
rise to different relative measures of time and length as
determined by two observers in motion.
, is constant with respect to all
observers, independent of velocity. This makes light a very different
phenomenon from objects with mass that have different apparent
velocities depending on the motion of the observer. This result gives
rise to different relative measures of time and length as
determined by two observers in motion.
- The above postulates gave rise to Einstein's famous
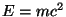 law
relating the equivalence of mass of energy.
law
relating the equivalence of mass of energy.
- Although Einstein's Theory of Relativity produced different
results from Newton for velocities near light and for strong gravity,
it completely agrees with Newton for lower velocities and gravity
fields like that on Earth.
The Curvature of Space-time
- Einstein's recognition that time was measured differently for
different relative observers led him to treat time as a fourth
coordinate in describing an event - one needs to have 4
dimensions to specify an event including
 &
&  where
where 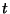 is
time. For example, we see the Sun as it was 8 minutes ago. Einstein
unified the concepts of space & time together as space-time.
is
time. For example, we see the Sun as it was 8 minutes ago. Einstein
unified the concepts of space & time together as space-time.
- Einstein did not use the concept of force to understand motions
in a gravitational field. Instead, his theory of gravity is a theory
that involves the geometry of space-time.
- When no masses are present, the geometry of space-time is flat.
A 2-dimensional analog is a flat, frictionless table top. Start a
ball moving at a given velocity across the table. It will continue to
move in a straight line at that velocity following the simple flat
geometry of the table. The same is true for 4 dimensional space-time.
- Now, when a mass is present, this mass produces a curvature of
space-time. The 2-dimensional analog would be a stretched piece of
thin rubber with an indentation at the center where the mass is
located. Let a ball go near the edge of the indentation & it will
accelerate toward the bottom. If you give the ball a little velocity
in a tangential direction, it will ``orbit'' the indentation. Thus,
the basic observed features of motion in a gravitational field can be
understood through this theory of curved space-time.
- Keep in mind that time, also, will flow differently depending
upon the location of the observer on this curved, 4-dimensional
space-time.
Black Holes
- Einstein's Relativity Theory predicts that the larger the mass,
the greater the curvature (or indentation) of space-time. A black hole
is the extreme example in which the indentation is infinitely deep.
- Consequences include:
- At the ``event horizon'' or Schwarzschild radius of
a black hole, the escape velocity is equal to the speed of light. For
an object with the mass of the Sun, this radius is only 1.5 km; for an
object with
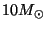 , this radius is 15 km.
, this radius is 15 km.
- Once an object falls inside the event horizon, it can never come
back out. It is lost forever to us. This includes light which is the
reason we call this object a ``black hole''.
- Although time would appear to run normally for an astronaut
approaching a black hole, an outside observer would judge that the
astronaut's clock is running slowly. In fact, that outside observer
would see that it would appear to take an infinitely long time for the
astronaut to fall into the black hole at the event horizon. This is
due to the extreme curvature of space-time near the black hole.
- It is important to note that although the gravity within a few
Schwarzschild radii of a black hole is very large, beyond this
distance the strength of gravity drops to that predicted by Newton for
an object of mass
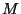 . That is, the gravity force (in Newton's terms)
drops as
. That is, the gravity force (in Newton's terms)
drops as 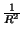 , where
, where 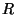 is the distance from the black
hole.
is the distance from the black
hole.
- How does a black hole form? For stars at the end of their lives
(after Red Giant & supernova stages) which are
 5
5 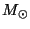 ,
there is no barrier to total gravitational collapse. The gravity is
strong enough to overcome the degenerate gas pressure which halts the
collapse of lower mass white dwarfs & neutron stars. The volume
becomes very small and the density is infinitely large. The resulting
curvature of space-time is infinitely deep & the object becomes a
black hole.
,
there is no barrier to total gravitational collapse. The gravity is
strong enough to overcome the degenerate gas pressure which halts the
collapse of lower mass white dwarfs & neutron stars. The volume
becomes very small and the density is infinitely large. The resulting
curvature of space-time is infinitely deep & the object becomes a
black hole.
- Have we ever seen a black hole? Since the black hole
Schwarzschild radius is small & the hole is black, we cannot hope to
directly observe the hole. However, we can possibly see it through
the strong gravitational effects it has on nearby objects. A black
hole in a binary star system with a Red Giant companion will accrete
gas from the companion; the resulting accretion disk will heat &
produce X-rays. The Cygnus X-1 star system is a good candidate for a
black hole; it has a visible Red Giant star and an invisible companion
with an inferred mass of
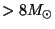 using Kepler's 3rd Law.
using Kepler's 3rd Law.
Other Observational Consequences of Relativity
- Light must follow the curvature of space-time like any object
with mass. So, the path of light in the vicinity of a massive object
will curve toward the object. This is not expected from Newton's Law
of Gravity.
- The deflection of starlight near the Sun was observed for the
first time during the solar eclipse of 1919.
- Subsequently, the VLA has been used to measure the deflection of
radio waves from distant radio sources near the Sun.
- Another consequence of Relativity is that galaxies can act as
gravitational lenses on images of more distant galaxies or
quasars. Light from a more distant galaxy bends toward a nearby
galaxy on its way to us. The result is a distortion of the image of
the more distant galaxy much like a lens. This can produce multiple
images of the distant galaxy or even a ``ring'' of light.
Cosmology
What Is Cosmology?
- Cosmology is the study of the physical Universe's nature &
evolution. It involves the origin and evolution of the Universe and
the structure within the Universe.
- General facts and assumptions used in cosmology include:
- The Universality of Physical Laws - Newton's Laws,
Kepler's Laws, Einstein's Relativity, etc. are assumed to hold on
Earth and everywhere else in the Universe.
- Cosmological Principle - The Universe is homogeneous
(matter is uniformly spread throughout space) and isotropic (the
Universe is the same in all directions) on very large scales. This is
not an assumption
The Hubble Law
- Edwin Hubble in 1929 discovered a direct relationship between
the velocity of a galaxy (redshift) and distance. It is expressed as
where 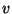 is the galaxy velocity (measured from the Doppler shift of
galaxy spectral lines),
is the galaxy velocity (measured from the Doppler shift of
galaxy spectral lines), 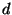 is the galaxy distance, and
is the galaxy distance, and 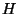 is today
called the Hubble constant. This Law implies that the Universe
is not static but is expanding and probably evolving in
time.
is today
called the Hubble constant. This Law implies that the Universe
is not static but is expanding and probably evolving in
time.
- Hubble's conception of the Universe is that all galaxies are
rushing away from us and each other (this is why we see only redshifts
for galaxies).
- In Einstein's view, the Hubble Law is the result of the
expansion of space-time. It is an expansion of the geometry of the
Universe and not simple recession of galaxies. The Universe is like a
raisin bread that is rising in the oven, where the raisins are galaxies.
The Steady State Model
- Throughout the 1950's and early 1960's, the most popular model
of the Universe was the Steady State model.
- The Steady State model assumes the Perfect Cosmological
Principle in which the Universe is the same at all times and in all
locations. Thus, the Universe had no beginning and will have no end.
- For this to be true in light of the Hubble expansion, there must
be continuous creation of matter to keep the average density of the
Universe constant. This requires about 1 hydrogen atom per liter
every billion years to ``pop'' into existence.
The Big Bang Model
- An alternative model first proposed in the late 1940's is today
called the Big Bang. It requires the Universe to have a
definite beginning about 15 billion yrs ago. At that time, all
matter, photons, and space was compressed into an infinitesimally
small region.
- This small volume suddenly erupted, creating an expanding
space-time that we see today. In this model, there is no center or
edge of the Universe. The Universe began everywhere at the same
time.
- In the earliest epochs, the Universe was very hot. It resembled
an extremely hot blackbody. The model predicts that as the Universe
expands, the temperature of this cosmic or primordial background
radiation will decrease.
- In 1964, A. Penzias and R. Wilson from Bell Laboratories
accidentally discovered this radiation while making very sensitive
observations of the sky with a new radio receiver and telescope. More
recent measurements by NASA's COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer)
satellite has confirmed that the broad spectral shape of this
background radiation perfectly matches a blackbody and has a
temperature of 2.74 K.
- The background radiation matches well the predictions of the Big
Bang. However, it conflicts with the Steady State model because this
radiation shows that the Universe has cooled and evolved with time;
therefore, it violates the perfect cosmological principle.
- The energy of the Universe was dominated by radiation for the
first 100,000 yrs. After this time, the Universe cooled enough to
become transparent to radiation. Matter formed into protons and
atoms. These eventually combined to produce the larger scale
structures previously discussed.
The Inflation Model
- At a very early moment, the Universe had a phase of VERY fast
expansion (``inflation''). Energy of the vacuum was the source of the
expansion. Once upon a time the vacuum ruled. At the beginning was vacuum.
- Inflation ended with heating the Universe to a very high
temperature. That was the beginning of the Big Bang
How Will It All End?
- The future of the Universe depends upon the geometry of
space-time which in turn depends upon the total mass and average
density within the Universe. Since dark matter appears to be the
dominant form of mass in the Universe, its density will determine the
future history of the Universe.
- If the density is above a critical value (
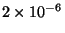 atoms/cm
atoms/cm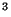 ), the Universe will curve back upon itself (like a giant
sphere in two dimensions). The gravity will be large enough to halt
the expansion of the Universe, causing it to eventually re-collapse
into a Big Crunch. This is called a Closed Universe.
), the Universe will curve back upon itself (like a giant
sphere in two dimensions). The gravity will be large enough to halt
the expansion of the Universe, causing it to eventually re-collapse
into a Big Crunch. This is called a Closed Universe.
- If the density is below this critical value, the Universe will
continue to expand forever. This is called an Open Universe.
- If the density of the Universe is exactly at the critical value,
this is called a Flat Universe because the geometry of space-time
is flat. The Universe is effectively infinite.
- Thus, the answer to ``How will the Universe end?'' will be known
only after we understand the nature and density of the dark, unseen
matter which gravitationally rules the Universe.



Next: About this document ...
2003-08-25